The Google Pixel Watch 3: Addressing Size Concerns and Enhancing Features
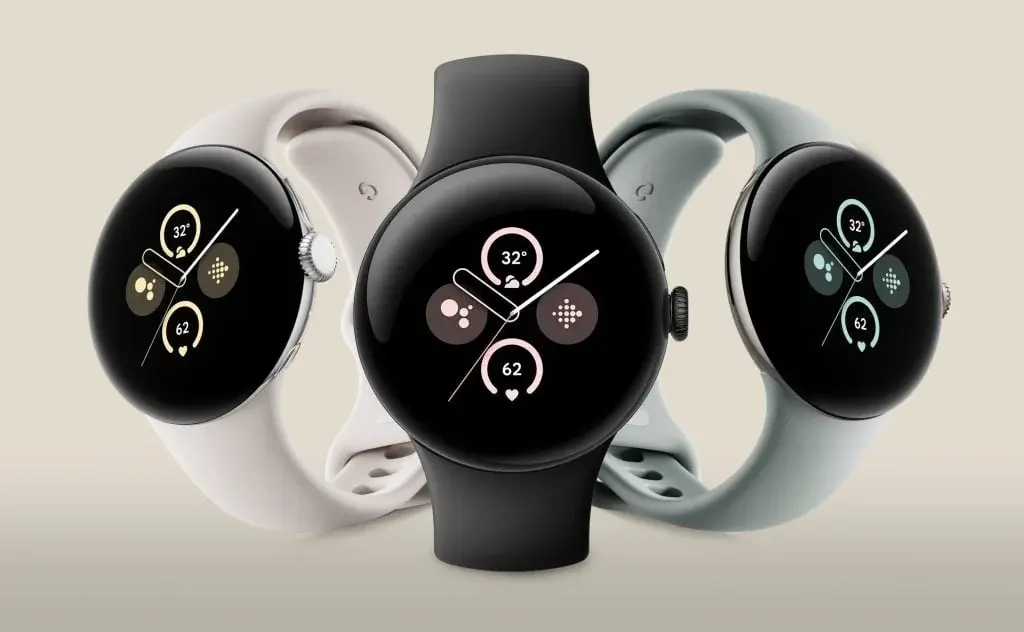
The Google Pixel Watch 3 is poised to tackle a recurring issue seen in its previous iteration – its compact size. In stark contrast to competitors such as Samsung, which deliver more spacious alternatives reaching up to 47mm, the Pixel Watch 2 remains confined to a 41mm option. Nevertheless, Google is anticipated to introduce two size variants for the Pixel Watch 3, furnishing a remedy for individuals favoring a larger smartwatch.
Enhanced Dimensions and Feature Set
Though the precise dimensions of the Pixel Watch 3’s cases remain unconfirmed, the larger variant is projected to surpass the 41mm footprint of the Pixel Watch 2. This upsize could facilitate a larger screen, possibly reaching 1.3 inches, and accommodate a beefier battery, consequently elevating battery longevity. Moreover, the expanded casing might house a broader array of health sensors, amplifying the watch’s functionality.
Refined Aesthetics and Interoperability
The enlarged iteration of the Pixel Watch 3 is expected to sport 22mm bands, trumping the 20mm bands utilized in the current model. This alteration in band dimensions could contribute to a more streamlined appearance for the timepiece. Furthermore, trimming the bezel encircling the screen could further elevate the overall visual appeal of the device.
Suited for Larger Wrists and Prolonged Battery Performance
The advent of a larger Pixel Watch would cater well to individuals with more substantial wrists and those who prioritize enduring battery life. While the Pixel Watch 2 already boasts a 24-hour battery span with its ever-active display feature, a grander model may likely deliver even more robust battery efficiency, meeting the demands of users necessitating prolonged usage sans frequent recharges.
Launch Schedule and Technological Aspects
The advent of the Pixel Watch 3 is anticipated in early October, aligning with Google’s tradition of unveiling new gadgets alongside their Pixel mobile series. Concerning technology, the Pixel Watch 3 is presumed to leverage the identical Snapdragon W5 chipset as its forerunner, given the absence of reports suggesting a fresh chipset explicitly tailored for Wear OS.
In summary, the forthcoming Google Pixel Watch 3 seeks to resolve the size limitation evident in its precursor by introducing two size selections. The larger rendition is anticipated to offer an expanded display, enhanced battery life, and an augmented suite of health sensors. With a more elegant design and compatibility with broader bands, the Pixel Watch 3 is set to accommodate individuals with heftier wrists. The launch date is set for early October, coinciding with the introduction of the new Pixel 9 series.