Key Takeaways
1. Huawei is finding new ways to obtain advanced hardware for AI training despite TSMC blocking its chip production efforts.
2. The newly released Ascend 910C shows potential to compete with Nvidia, but has significant limitations.
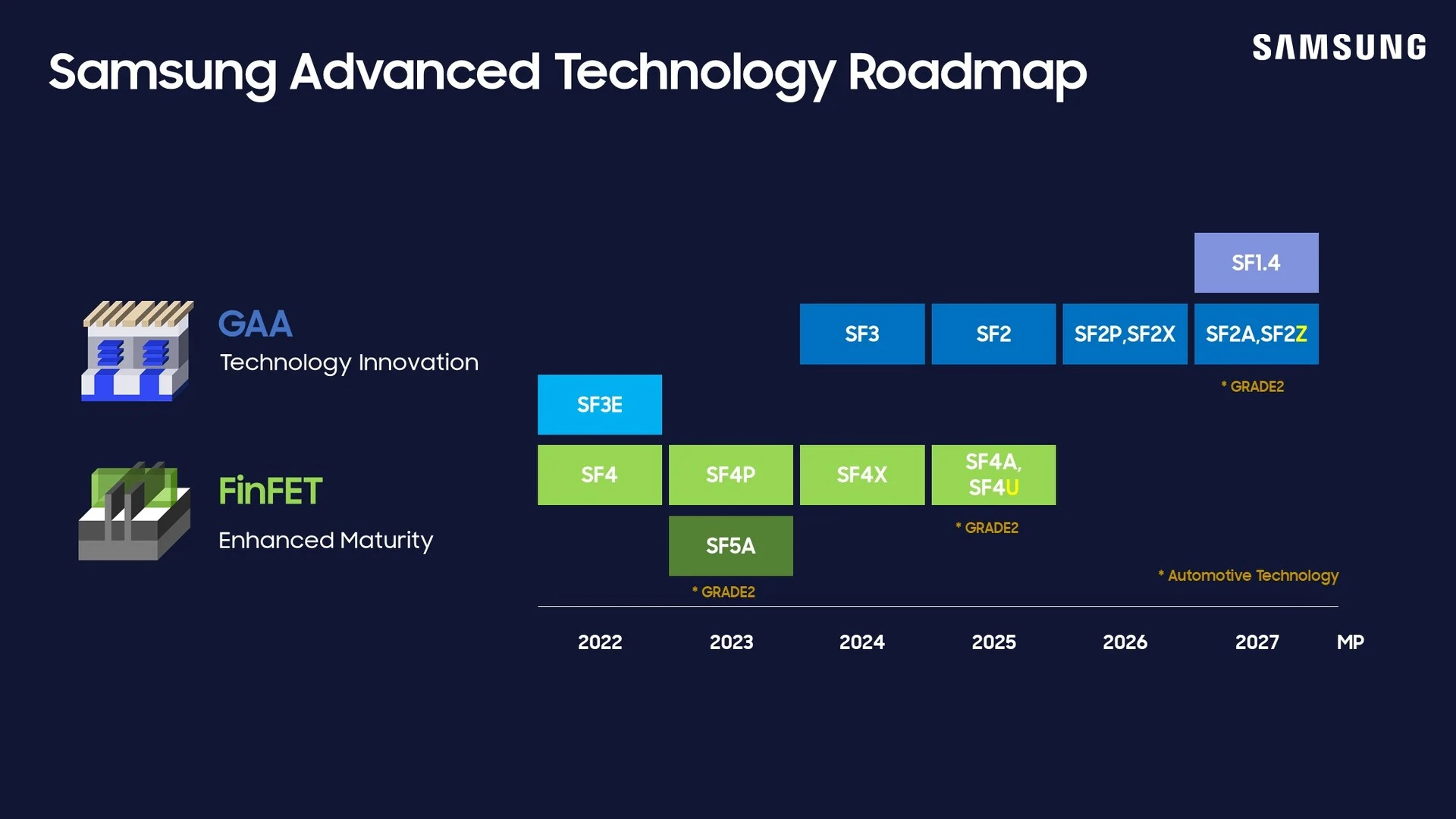
3. The Ascend 920 chip is expected to launch soon, built using SMIC’s 6 nm class N+3 technology, with mass production starting in the latter half of 2025.
4. The Ascend 920 is designed to deliver 900 TFLOPS of BF16 performance and 4,000 GB/s memory bandwidth with HBM3 memory.
5. SMIC’s 6 nm class node may also be used in future products like Kirin chips for Huawei smartphones, with whispers of a developing 5 nm class node.
Even with TSMC blocking Huawei’s efforts to produce its Ascend 910B chips using advanced technology, the large Chinese company has discovered new methods to obtain top-tier hardware for AI training. The Ascend 910C was released shortly after that setback, and a detailed analysis from SemiAnalysis indicates that it has the potential to compete with Nvidia, though there are several important limitations. Recently, a report from DigiTimes indicates that its successor, the Ascend 920, is expected to launch soon.
Manufacturing Insights
Well-known leaker Jukanlosreve on X has shared that the Ascend 920 will be built using SMIC’s 6 nm class N+3 technology. Mass production is set to begin in the latter half of 2025. The chip is said to deliver 900 TFLOPS of (presumably) BF16 performance and boasts a memory bandwidth of 4,000 GB/s, made possible by HBM3 memory. It is designed to replace Nvidia’s Hopper-based H20 chip, which has recently been banned for use in China.
Future Developments
The introduction of the Ascend 920 also marks the debut of SMIC’s new 6 nm class node, which is likely to be implemented in other products, including Kirin chips for Huawei smartphones. Although the previously anticipated Kirin 9100 didn’t succeed, there are indications that it may still launch later this year. Additionally, there have been whispers about a 5 nm class SMIC node under development, but advancements in that area may be sluggish due to limited access to EUV machinery.
Source:
Link