Google recently hinted at its plans for the upcoming Pixel 8a while discussing a change in a recent Pixel software update. The tech giant revealed that a new battery stats page will be exclusive to the Pixel 8a and future devices.
Google's Battery Stats Update
Android 14 QPR1 initially introduced a feature showcasing charging cycle counts and the battery's manufacturing date. However, users noticed that this feature disappeared in the March 2024 Pixel update.
Clarification and Future Devices
In response to inquiries, Google explained on a bug tracker page that the battery stats feature was meant for upcoming devices. The company stated that the page is specifically enabled for Pixel 8a and beyond, indicating that this was intentional.
Insights and Speculations
Google's statements not only confirm the imminent arrival of the budget-friendly Pixel 8a but also hint at a more robust battery health monitoring system for future Pixel devices. This enhancement, however, will not be extended to older Pixel models.
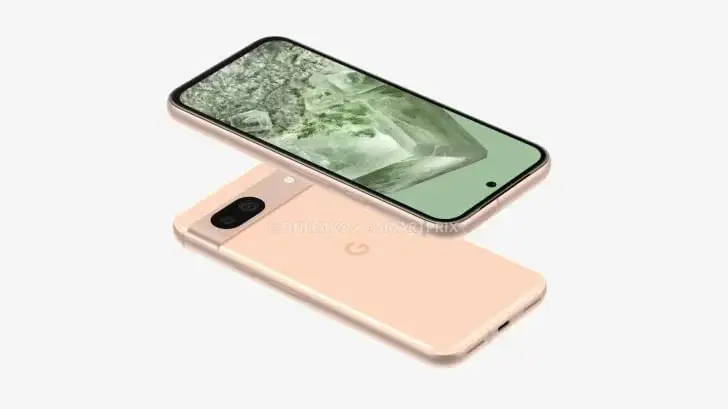
The Pixel 8a is anticipated to be launched in the coming months, potentially coinciding with Google I/O in May, following the release schedule of its predecessors.
Here: This timeframe could align with the release pattern of its predecessors.
Rumored Specifications
Rumors surrounding the Google Pixel 8a suggest it might feature the Tensor G3 chip, possibly a modified version of the chip used in the flagship Pixel 8 series. The device is rumored to offer 8 GB of RAM and support 27W fast charging. Last year, leaked CAD renders revealed the Pixel 8a's dimensions as 152.1 x 72.6 x 8.9mm, with a 6.1-inch OLED display. Further details about the smartphone are yet to be unveiled.