Key Takeaways
1. Xiaomi has launched its first open-source AI system, MiMo-7B, designed for complex reasoning tasks and excelling in mathematics and code generation.
2. MiMo-7B has 7 billion parameters and competes effectively with larger models from OpenAI and Alibaba, especially in mathematical reasoning and coding contests.
3. The model’s training involved a comprehensive dataset of 200 billion reasoning tokens, using a multi-token prediction goal to enhance performance and reduce inference times.
4. Post-training enhancements include unique algorithms for reinforcement learning and infrastructure improvements that significantly boost training and validation speeds.
5. MiMo-7B is available in four public variants, with notable performance benchmarks in mathematics and coding, and it can be accessed on Hugging Face and GitHub.
Xiaomi has quietly entered the large language model arena with its new MiMo-7B, marking its first open-source AI system for the public. Created by the recently formed Big Model Core Team, MiMo-7B is designed for complex reasoning tasks and excels beyond rivals like OpenAI and Alibaba when it comes to mathematical reasoning and code generation.
Model Specifications
As indicated by its name, MiMo-7B has 7 billion parameters. Even though it is much smaller than many leading LLMs, Xiaomi asserts that it competes equally with larger models such as OpenAI’s o1-mini and Alibaba’s Qwen-32B-Preview, all of which are capable of AI reasoning.
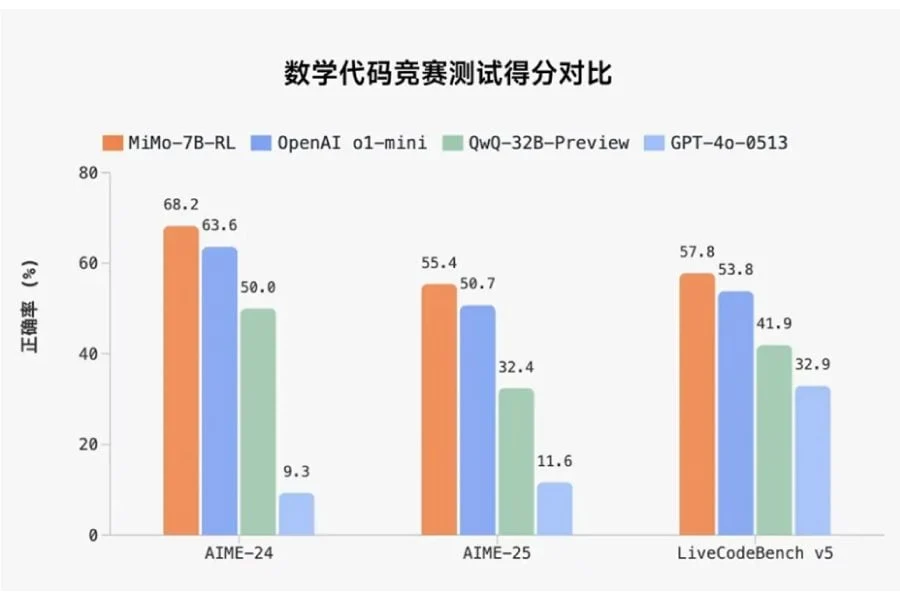
Xiaomi MiMo-7B surpasses OpenAI and Alibaba’s models in mathematics reasoning (AIME 24-25) and code contests (LiveCodeBench v5).
Training Details
The foundation of MiMo-7B is a rigorous pre-training schedule. Xiaomi claims to have created a comprehensive dataset consisting of 200 billion reasoning tokens and has provided the model with a total of 25 trillion tokens through three phases of training.
Instead of the conventional next-token prediction, the company opted for a multi-token prediction goal, which they say reduces inference times without compromising the quality of the outputs.
Post-Training Enhancements
The post-training phase combines various reinforcement learning methods alongside infrastructure enhancements. Xiaomi developed a unique algorithm called Test Difficulty Driven Reward to mitigate the sparse reward challenges often seen in RL tasks involving intricate algorithms. Moreover, they introduced an Easy Data Re-Sampling technique to ensure stable training.
On the infrastructure side, Xiaomi has created a Seamless Rollout system to minimize GPU downtime during both training and validation. According to their internal metrics, this results in a 2.29× increase in training speed and almost a 2× boost in validation performance. The rollout engine also supports inference methods like multi-token prediction in vLLM settings.
Availability and Performance
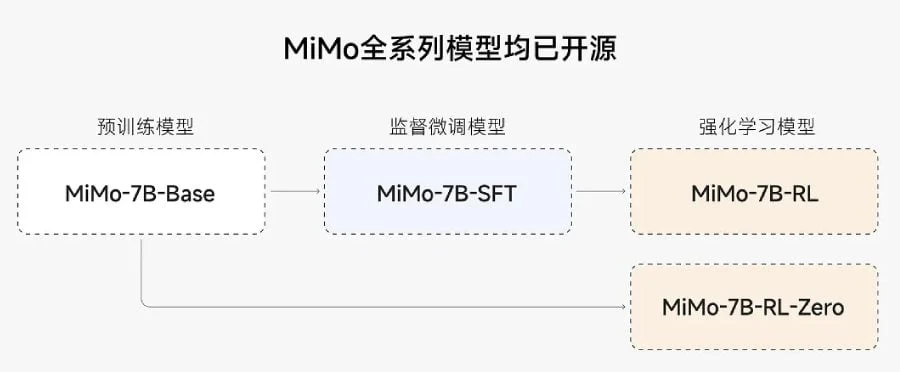
Now, MiMo-7B is open source with four public variants available:
– Base: the unrefined, pre-trained model
– SFT: a version refined with supervised data
– RL-Zero: a variant enhanced through reinforcement learning starting from the base
– RL: a more refined model based on SFT, claimed to offer the best accuracy
Xiaomi has also shared benchmarks to support its claims, at least theoretically. In mathematics, the MiMo-7B-RL variant is said to achieve 95.8% on MATH-500 and over 68% on the 2024 AIME dataset. Regarding code, it scores 57.8% on LiveCodeBench v5 and nearly 50% on version 6. Other general knowledge tasks like DROP, MMLU-Pro, and GPQA are also included, though scores hover in the mid-to-high 50s—respectable for a model with 7 billion parameters, yet not groundbreaking.
MiMo-7B can now be accessed on Hugging Face under an open-source license, and all relevant documentation and model checkpoints are available on GitHub.