Key Takeaways
1. Huawei’s HarmonyOS is now independent, stopping the use of Google code and focusing on its own ecosystem.
2. HarmonyOS 5 aims to replace Windows on laptops and desktops, boasting a similar framework to its smartphone version.
3. The user interface features a taskbar and quick settings menu, resembling Microsoft’s design, with an AI feature for document interaction.
4. Multitasking capabilities allow users to view open windows side by side, enhanced by modern design elements like dynamic lighting and animated wallpapers.
5. HarmonyOS 5 offers seamless connectivity with HarmonyOS mobile devices but may not support apps for Western markets.
Ever since the US imposed sanctions, the Chinese technology company Huawei has been working on its own operating system named HarmonyOS. The initial versions were based on the Android Open Source Project, but since the launch of HarmonyOS Next, Huawei has stopped using any Google code. This means that their smartphones and smartwatches, particularly those for the Chinese audience, do not have any US software. Now, HarmonyOS 5 is set to take the place of Windows on laptops and desktop computers.
Structure and Performance
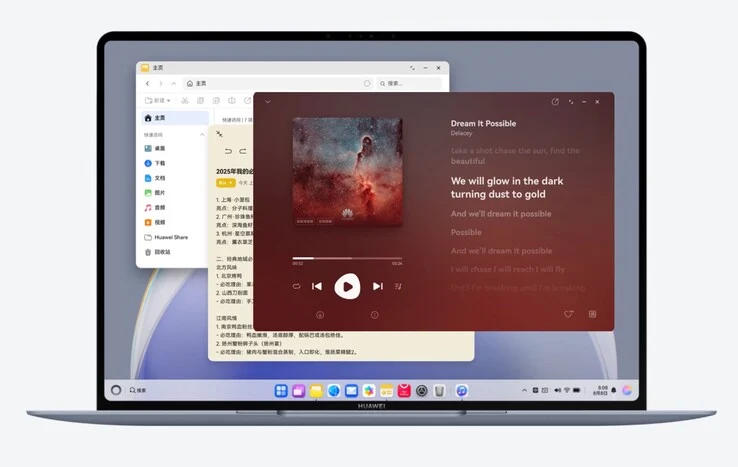
The PC version of the operating system shares a similar framework with the smartphone version. It includes the HarmonyOS Kernel, StarShield security software, and the Ark Engine, which is said to enhance performance. Huawei claims that this operating system is “faster than Windows,” although they did not share any specific evidence to support this assertion. The user interface, however, seems to be inspired by Microsoft’s lead OS, featuring a taskbar at the bottom of the screen along with a desktop filled with applications, documents, and widgets.
User Interface and Features
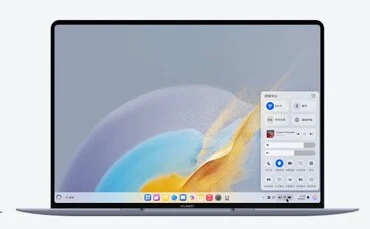
In the center of the taskbar, there are pinned apps, while crucial information such as the time and battery percentage can be seen on the right. Tapping these icons brings up a quick settings menu that resembles the HarmonyOS found on smartphones. The button located at the far right opens an AI feature, which appears as a window on the right edge of the display and operates like a chatbot, interacting with documents and applications, much like Microsoft Copilot does.
Multitasking and Connectivity
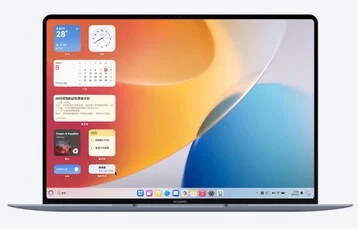
HarmonyOS 5 is packed with multitasking options, allowing users to view all open windows side by side by swiping up on the trackpad with three fingers. Huawei has incorporated modern touches, like dynamic lighting effects that respond to the mouse pointer and animated wallpapers, to give it a fresh feel.
Like macOS and iOS, HarmonyOS 5 can connect effortlessly with smartphones and tablets that utilize the mobile version of HarmonyOS. For example, users can type a message on their phone using the laptop’s keyboard or copy a file from a tablet and paste it onto their computer. Huawei has also pledged a broad range of app support from third-party developers. However, similar to HarmonyOS Next, it’s quite improbable that HarmonyOS 5 will be compatible with devices meant for Western markets.
Source:
Link