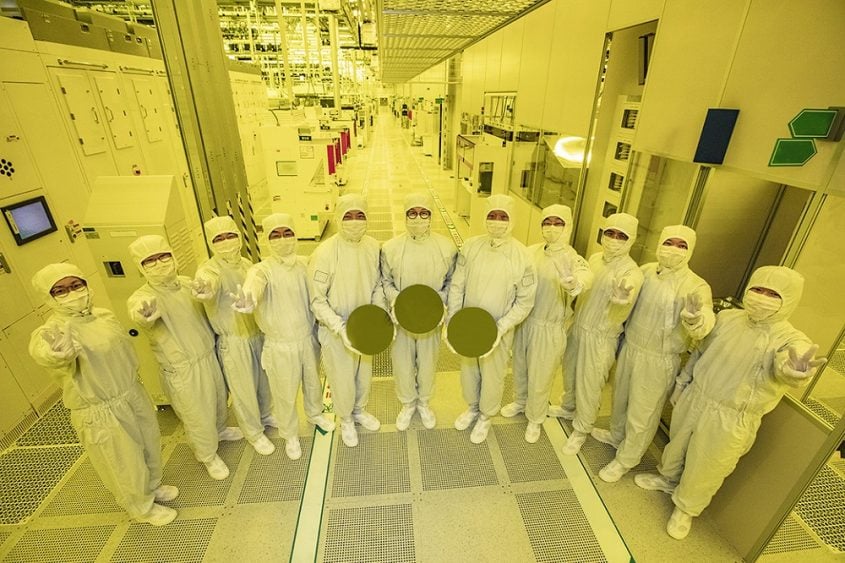
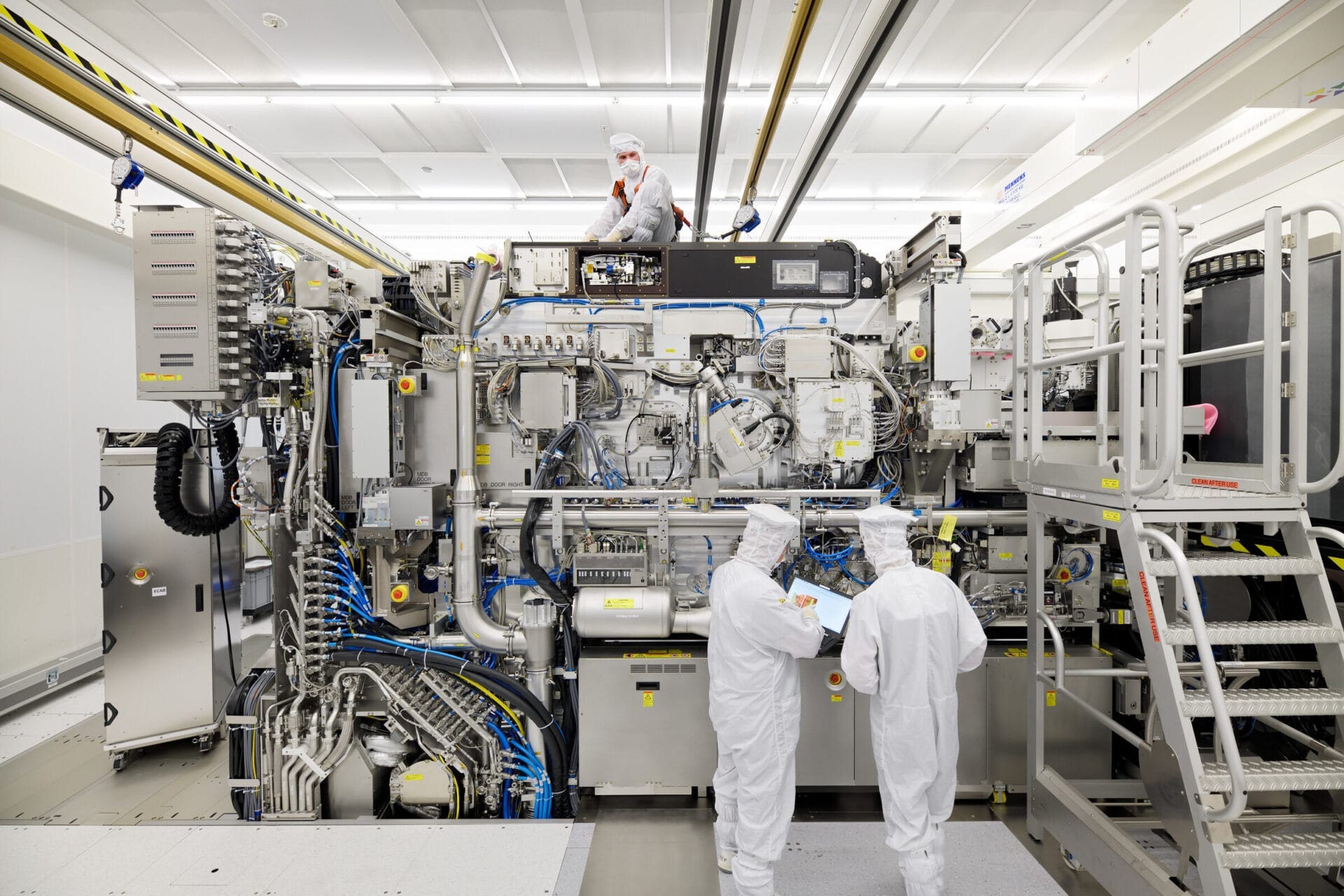
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) is set to introduce its 2-nanometer chip-making technology at its facilities in Arizona around 2028, as stated by Wu Cheng-wen, the head of Taiwan’s National Science and Technology Council (NSTC).
Timeline and Regulations
This schedule is in line with Taiwan’s rules, which require a three-year delay between the production of advanced semiconductor technology domestically and internationally. TSMC aims to begin large-scale production of 2nm chips in Taiwan by 2025, with initial test production already taking place at its site in Hsinchu County.
Arizona Expansion Plans
The expansion in Arizona will feature three fabrication plants (fabs). The first fab is expected to kick off production of 4nm chips in early 2025. The second fab is preparing to manufacture 3nm and 2nm chips starting in 2028. The third facility, which is part of a potential $6.6 billion subsidy agreement, will focus on 2nm technology or even more advanced options, with production anticipated to commence by late 2030.
Progress in Taiwan
Meanwhile, TSMC is also advancing its 2nm production in Taiwan. The Baoshan plant in Hsinchu County is planned to enter full production in 2025, followed by another plant in 2026. Additionally, a facility in Kaohsiung is on track to begin production in 2026, while another one is currently under construction.
Just last month, TSMC received final approval for $6.6 billion in funding via the CHIPS Incentives Program. This agreement will help bring forth A16 technology, which incorporates advanced nanosheet architecture and a feature known as Super Power Rail tech. These enhancements will increase chip efficiency by allowing more logic to fit while also improving power delivery.
Oversight and Strategy
The transfer of cutting-edge technologies overseas is under strict scrutiny. Taiwan’s Ministry of Economic Affairs is closely watching the situation, emphasizing that TSMC must achieve domestic production of its most sophisticated processes before contemplating any overseas ventures. This approach helps Taiwan maintain its lead in the technology sector while supporting allied nations in boosting their semiconductor manufacturing capabilities.