Key Takeaways
1. Hybrid Battery Project: China launched its first hybrid battery project combining sodium-ion and lithium cells to enhance energy storage capabilities.
2. Energy Storage Capacity: The facility in Yunnan province has a capacity of 400 MWh, aimed at stabilizing energy from wind and solar farms connected to the Southern Power Grid.
3. Improved Technology: The sodium-ion batteries used have a response speed six times faster than traditional sodium batteries, improving management of renewable energy fluctuations.
4. Cost-Effective and Safe: Sodium batteries are less expensive, safer, and perform better in extreme temperatures compared to typical lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries.
5. Significant Output: The system provides a steady output of 200 MW and can power around 270,000 homes with up to 98% renewable energy annually.
After the successful rollout of energy storage initiatives utilizing sodium-ion batteries to stabilize the electricity grid, China has now launched its first hybrid battery project.
Combining Battery Technologies
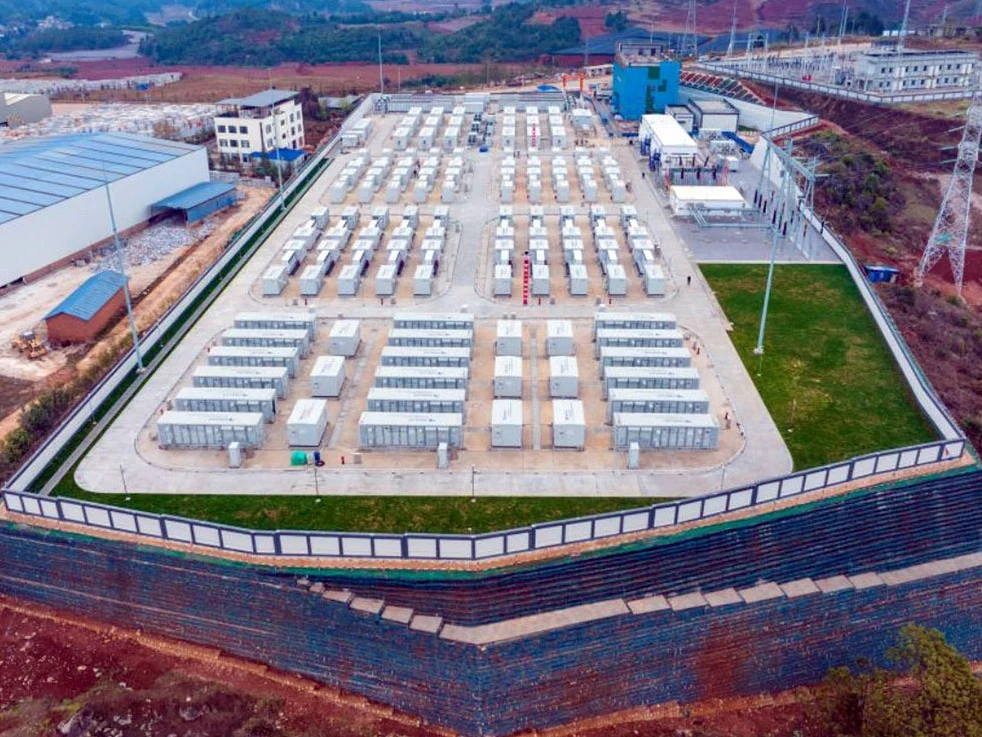
This innovative project incorporates both sodium-ion and lithium cells, leveraging the unique advantages of each type. Located in Yunnan province, the energy storage facility has a remarkable capacity of 400 MWh, designed to store the fluctuating energy generated by wind and solar farms connected to the Southern Power Grid. This development aims to mitigate the kind of system strain from renewable sources that contributed to recent blackouts in Southern Europe.
Advanced Battery Features
The hybrid lithium-sodium energy storage system (ESS) relies on sodium-ion batteries provided by HiNa. They assert that their latest generation of high-capacity cells has a response speed that is six times quicker than traditional sodium batteries, a critical improvement for managing the unpredictable nature of renewable energy inputs.
Typically, energy storage projects utilize lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, commonly found in portable power stations like the Anker Solix C1000. In contrast, sodium batteries are not only less expensive but also safer, provide faster output, and have better capacity retention in extreme temperatures. This makes hybrid ESS systems more durable and cost-effective.
Groundbreaking Achievement
HiNa proudly claims that this project is the first-ever multi-power composite sodium-ion battery energy storage system in the world. They had to develop a specialized grid-level power converter tailored specifically for the unique requirements of sodium batteries as part of the project.
The first high-capacity sodium-lithium energy storage station designed for grid use occupies a mere 0.012 square miles and has the capability to handle 580 million kWh annually. This amount of energy can power around 270,000 homes with up to 98% renewable energy all year long.
The sodium-lithium ESS delivers a steady output of 200 MW, aimed at stabilizing the peak output fluctuations from over 30 local wind and solar facilities. The system adjusts its charging and discharging modes in real-time based on the renewable energy input. It has been undergoing grid capacity tests since March and has now received certification to operate as a large-scale hybrid ESS featuring both sodium-ion and lithium batteries.
Source:
Link