Key Takeaways
1. Nvidia is in talks to invest in PsiQuantum, a start-up focusing on photonic quantum computers, but details of the deal are unclear.
2. PsiQuantum seeks at least $750 million in funding, with a pre-money valuation of around $6 billion, and BlackRock is already involved.
3. Nvidia’s strategy is evolving, as indicated by the establishment of a quantum-research lab in collaboration with Harvard and MIT.
4. PsiQuantum uses a unique method of creating photonic qubits with standard semiconductor processes, facilitating easier mass production.
5. Even if the investment happens, PsiQuantum’s technology is still experimental, and commercial quantum computers are not expected to be available immediately.
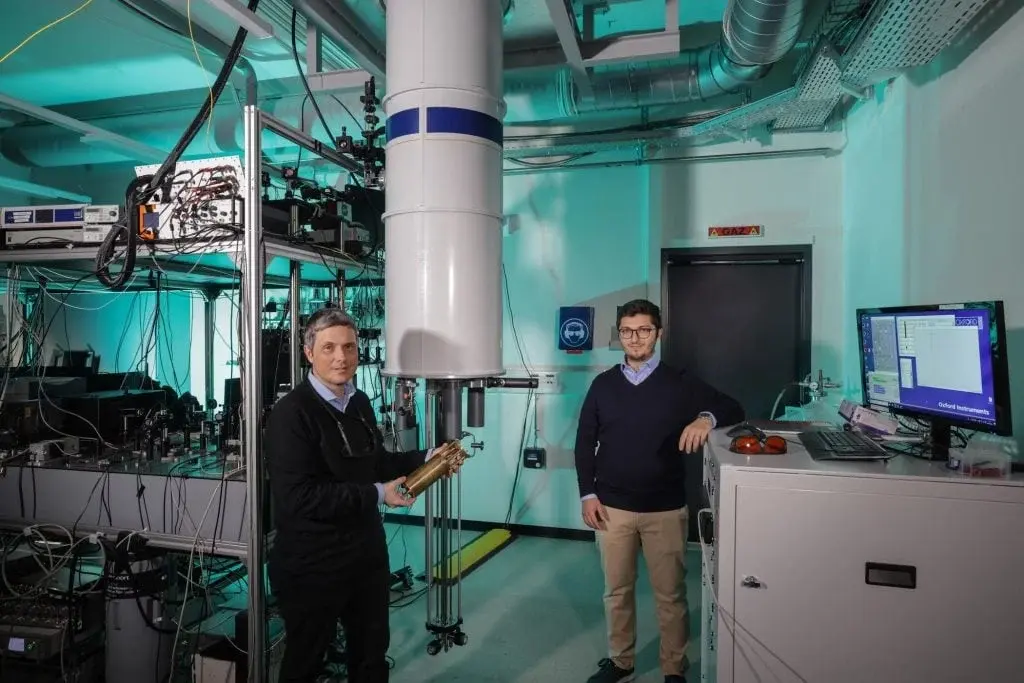
Nvidia is said to be deep in talks about investing in PsiQuantum, a start-up in Silicon Valley that’s working on big photonic quantum computers. The Information reports that discussions are going well, but neither Nvidia nor PsiQuantum has made any comments, leaving the specifics like size, structure, and timing of the potential deal unclear.
Investment Insights
This potential investment comes after a report from March, which stated that PsiQuantum is looking for at least $750 million, with a pre-money valuation around $6 billion, and that BlackRock is already involved. If Nvidia joins in, it would not only enhance the funds for the start-up but also connect it to Nvidia’s growing ecosystem in quantum software.
Nvidia’s Evolving Strategy
Nvidia’s attitude seems to be changing. Back in late 2024, CEO Jensen Huang launched a quantum-research lab in Boston with Harvard and MIT, even after saying that practical quantum computers were likely two decades away. These simultaneous initiatives imply that Nvidia might be preparing for a different timeline.
PsiQuantum takes a unique path compared to its competitors, who usually depend on superconducting or trapped-ion technology. The company creates photonic qubits using standard semiconductor processes, which could make mass production easier. They are already working with both federal and state agencies to set up two demonstration systems—one in Brisbane, Australia, and another in Chicago, Illinois.
Future Prospects
Even if the deal goes through, it won’t lead to a commercially viable quantum computer right away; PsiQuantum doesn’t have any products available, and the technology is still in the experimental phase. However, Nvidia’s interest highlights the strategic importance that major chip manufacturers now attribute to quantum computing as a potential next step or addition to traditional AI accelerators. All information is still tentative until an official announcement is made by the companies.
Source:
Link