For years, iPhone users have used enterprise certificates to install apps not approved by Apple’s App Store. Now, Huawei’s HarmonyOS NEXT seems to be adopting a similar strategy.
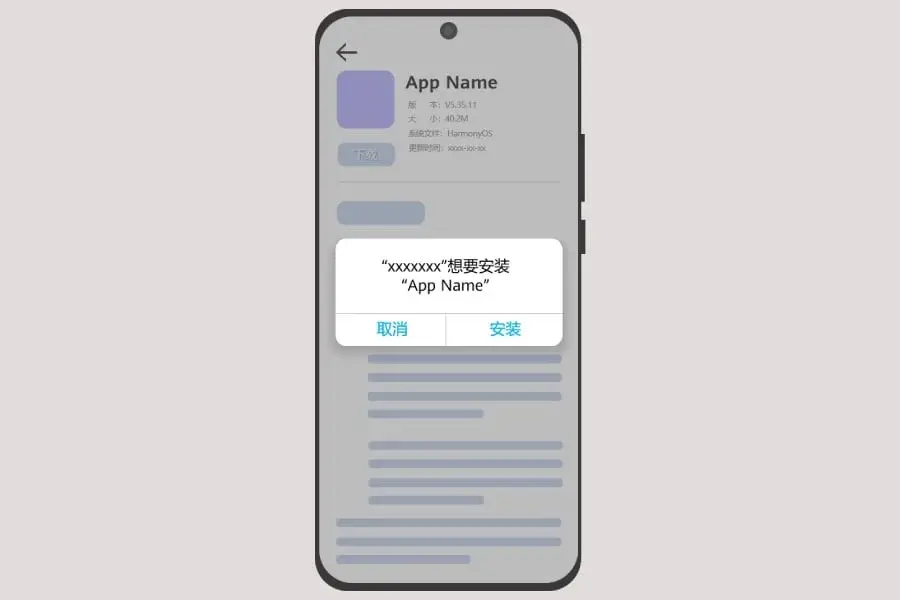
Recently, Huawei introduced a new method for sideloading apps on its OS. Developers will compile and package their apps with certificates and profiles issued internally by their organization.
Uploading and Installation
The final package and a description file are then uploaded to a server or cloud storage for users to download and install directly. These apps are designed for specific user groups, such as internal enterprise tools or programs.
Intended Use and Limitations
Huawei states that this feature is meant for “HarmonyOS applications that are not suitable or do not want to be publicly released on Huawei App Market.” Developers can also use Huawei’s AppGallery Connect (AGC) for small-scale distribution through designated channels.
However, this method has limitations. It currently supports only HarmonyOS apps built using the Stage model, and features like meta-services are not compatible yet. Users must manually enable the app by navigating to Settings > System > Enterprise Device and Application Management > Enterprise Application Management and granting permission.
Flexibility and Security Concerns
Huawei’s move isn’t surprising. Sideloading apps provides significant flexibility, especially for developers seeking to bypass App Market approval for specific use cases. However, it could also pose security risks. Unlike the curated App Market offerings, sideloaded apps lack official oversight, increasing the potential for malware or compromised software.

Leave a Reply