Key Takeaways
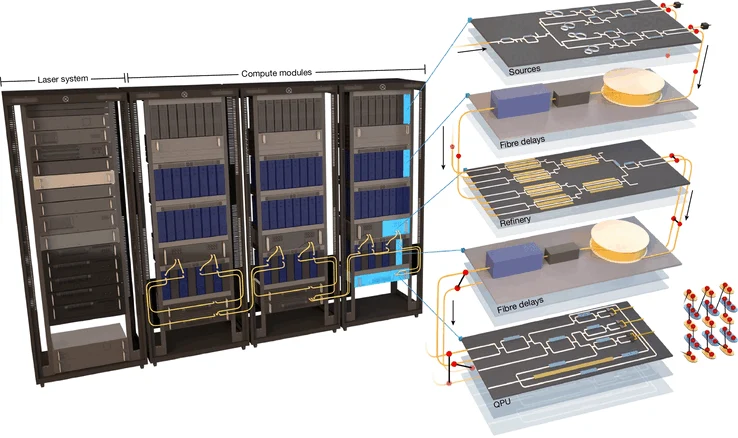
1. Introduction of Aurora: Aurora is the first modular photonic quantum computer designed for scalability, developed by Xanadu, a Canadian quantum tech company.
2. Addressing Key Challenges: Aurora improves fault tolerance and error correction while using light-based qubits, eliminating the need for extreme cooling typical in traditional quantum systems.
3. Expansion of Photonic Quantum Computing: Companies like PsiQuantum and startups like Quantum Source are exploring photonic quantum technologies to create efficient, commercially viable systems by 2027.
4. Sustainability in Quantum Technologies: The shift towards photonic quantum computing suggests a move towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly quantum technologies, supported by investments like NATO’s in Ephos.
5. Transformative Potential: The development of photonic quantum computing could significantly impact various industries and address complex challenges, marking a pivotal moment for practical quantum technologies.
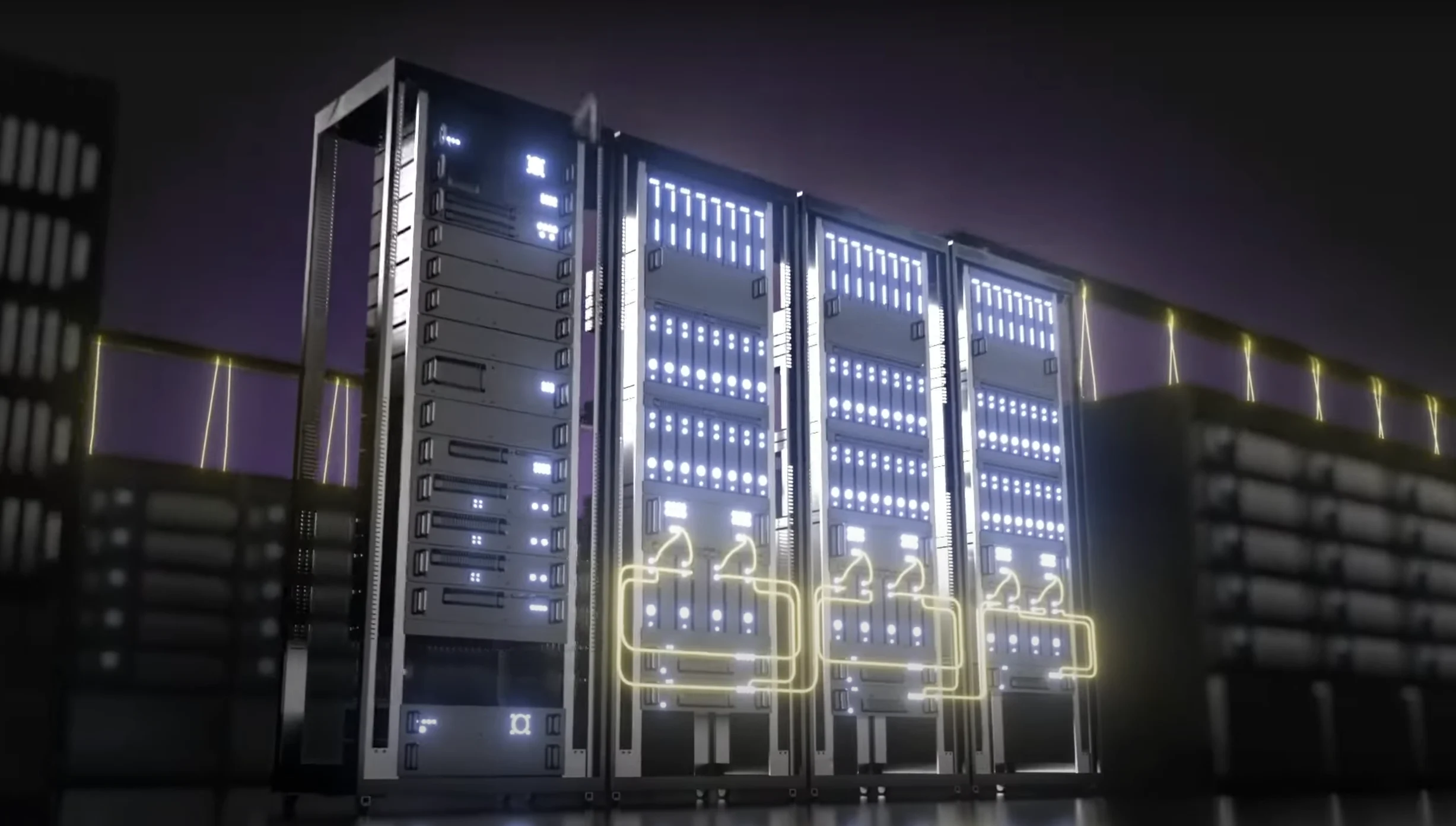
A major breakthrough in quantum computing is the introduction of Aurora, the first-ever modular photonic quantum computer that can function at scale with linked modules. Created by Xanadu, a Canadian firm specializing in quantum tech, Aurora utilizes photonic qubits for data processing, connected via fiber optic cables. This modular approach not only promotes scalability but also works well with current data center setups, which could change the game for quantum computing entirely.
Addressing Key Challenges
Aurora’s design tackles many old problems in quantum computing, such as fault tolerance and error correction. By using light-based qubits, Aurora avoids the necessity for extreme cooling that is common in traditional quantum systems. This breakthrough could lead to more practical and accessible quantum data centers, potentially speeding up progress in fields like cryptography, material science, and modeling complex systems.
Expanding the Horizons
The reach of photonic quantum computing goes beyond just Aurora. Companies like PsiQuantum are working on mass-producing quantum chips, aiming to create commercially viable quantum computers by 2027. Their method also utilizes photonics, using light particles for quantum calculations, which simplifies cooling needs. In a similar vein, startups like Quantum Source are investigating light-based quantum computing to create systems that are more efficient and can work at room temperature.
A Sustainable Future
The shift towards photonic quantum computing indicates a significant move towards more sustainable and scalable quantum technologies. As research and development progress, the incorporation of photonic systems might result in quantum computers that are not only more efficient but also friendlier to the environment, which aligns with worldwide efforts for sustainability in tech. Ephos, an Italian startup, has secured a $500,000 investment from NATO, aiming to achieve this goal with their glass-based integrated photonic circuits.
In conclusion, the emergence of photonic quantum computing, highlighted by innovations like Aurora, signifies a crucial moment in the search for practical and scalable quantum technologies. As these systems become increasingly integrated with existing infrastructures, they have the potential to transform industries and tackle complex challenges that were once thought to be insurmountable.
PsiQuantum, Nature, Xanadu, Reuters, Ephos.
Source:
Link


Leave a Reply