Key Takeaways
1. DeepSeek-R1-0528 outperforms its predecessor and rivals in cost-effectiveness and training speed.
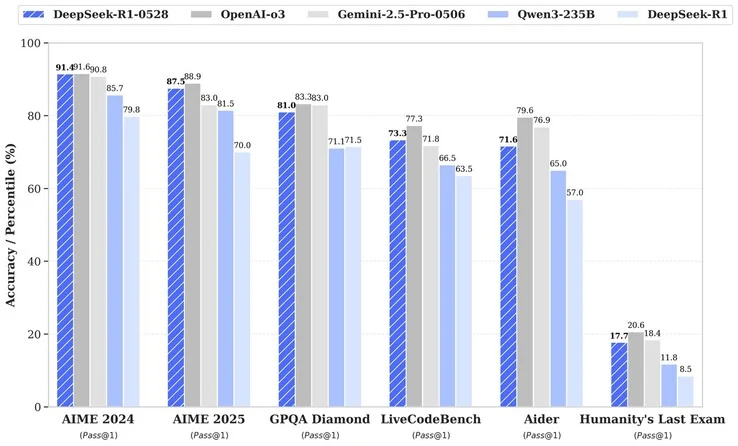
2. The model shows improvements in performance but only answers 17% correctly on the difficult Humanity’s Last Exam.
3. Enhanced training periods and fine-tuning contribute to the model’s better results, rather than major technological breakthroughs.
4. The new R1 model has fewer occurrences of AI hallucinations, providing more accurate information.
5. An open-source version of the R1 model is available, requiring an Nvidia 4090 GPU with 24 GB of memory for use.
DeepSeek has introduced the newest iteration of its innovative R1 AI large language model, named DeepSeek-R1-0528. The firm made its entrance into the AI sector with the releases of V3 and R1, both of which achieved top-ten performance in AI while being more cost-effective and quicker to train compared to rival models from companies like OpenAI and Google.
Performance Tests
The recent R1 model underwent evaluation using various AI benchmarks:
When compared to the initial release of R1, DeepSeek-R1-0528 shows better performance across all tests, although it only manages to answer 17% of the questions correctly on the challenging Humanity’s Last Exam. Since its main competitors also struggle on this particular test, the improvements seen in the latest DeepSeek R1 version are likely a result of extended training periods and fine-tuning rather than any major advancements in AI technology. A key highlight of the new R1 is its reduced instances of AI hallucinations, making it less prone to providing incorrect or misleading information.
Open-Source Availability
For those interested in exploring the open-source R1 model, it is possible to run distilled versions with eight billion parameters using an Nvidia 4090 GPU that has 24 GB of memory.
In summary, DeepSeek continues to push the boundaries of AI with its latest R1 model, making significant strides while maintaining affordability and efficiency. Users can find more about DeepSeek through its platforms, including DeepSeek news, DeepSeek Chat, and the DeepSeek R1 on GitHub.
Source:
Link