Key Takeaways
1. Over 3.2 million users were at risk due to malicious browser extensions that appeared legitimate but injected harmful scripts and stole information.
2. The attack involved a supply chain breach, allowing attackers to push harmful updates to trusted extensions without users’ knowledge.
3. Initial purposes of the affected extensions included ad blocking and screen capturing, but updates introduced unauthorized data theft and ad insertion.
4. Compromised developer accounts enabled attackers to gain control of extensions, exploiting permissions like ‘host_permissions’ and ‘scripting’.
5. Users should be cautious about installing new extensions and not rely solely on positive reviews, as traditional security protections may be evaded.
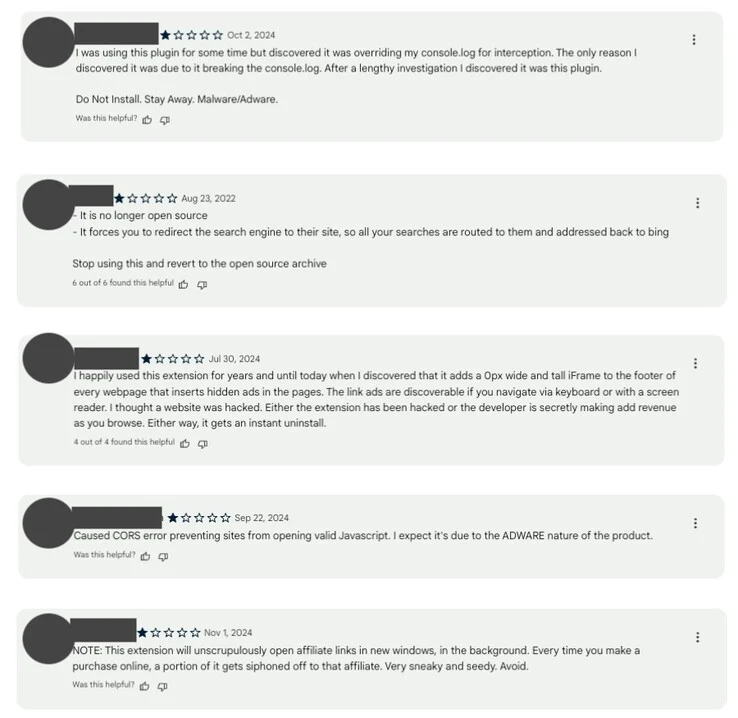
A significant security incident has put more than 3.2 million users at risk due to a series of harmful browser extensions. These extensions, which appeared to be legitimate, were discovered injecting malicious scripts, stealing user information, and committing search engine fraud. Researchers found that this attack was carried out via a supply chain breach, where attackers gained access to trusted extensions and pushed harmful updates without users being aware of it.
How the Malicious Extensions Operated
The affected extensions were initially created for purposes like ad blocking, emoji keyboards, and screen capturing, among others. However, updates added hidden scripts that allowed unauthorized data theft, modifications to HTTP requests, and the insertion of ads into webpages. Users who had previously given permissions to these extensions remained oblivious to these changes, which enabled attackers to manipulate their web activities in real-time. Many security experts have noted that the permissions these extensions required, such as host access and scripting controls, made them especially hazardous.
List of Affected Chrome Extensions
The investigation has linked this incident to developer accounts that were compromised. Some developers, without realizing it, transferred control of their extensions to the attackers, who then pushed malicious updates through the official browser extension stores. The attack’s framework seems connected to known phishing tactics. The threat actors exploited permissions like ‘host_permissions’, ‘scripting’, and ‘declarativeNetRequest’ to carry out their scheme.
Similarities to Past Attacks
Another alarming factor in this campaign is its similarity to earlier supply chain attacks, where trusted software is used as a vehicle for malware distribution. By using the update mechanisms of browser extensions, attackers can evade traditional security protections.
Currently, the identified extensions have been taken down from official platforms. Nonetheless, users should be cautious and not depend solely on positive reviews when deciding to install new extensions.
Source:
Link


Leave a Reply